Customers often ask me whether LCD and LED look alike, are they the same thing? As a senior engineer who has been engaged in the research and development of LED displays for a long time, I will analyze LED VS LCD from simple to in-depth based on the information I know.
First, let’s take a look at the definitions of the two:
LED VS LCD Definition
Definition of LED
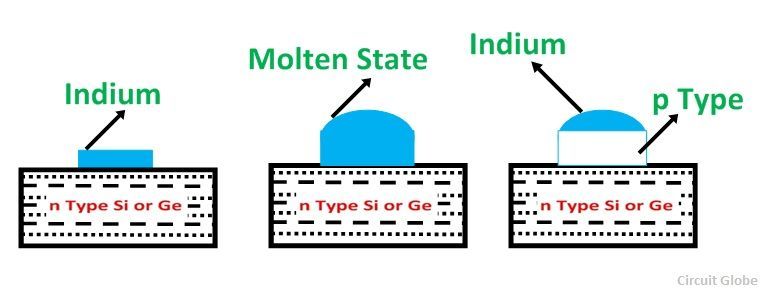
The complete form of LED is a light-emitting diode, so the light-emitting diode is the abbreviation of LED. An LED is a PN junction diode that emits light when current flows forward. LEDs are constructed by doping p-type and n-type materials. When power is applied to the LED, the P-type and N-type material charges will chemically react, the charges will recombine, and provide energy in the form of heat and light.
The material of semiconductors is translucent (allowing light to pass through) and it emits light through their junctions. The semiconductor material uses zinc arsenic compounds, which can produce red or yellow light. It is also available in green, red, and amber colors.
When multiple LED displays are combined, the distance from one of the lights to the other is measured. This distance is generally represented by the capital letter “P”. For example, the P2 LED display is the LED light to the other LED light. The distance is 2 mm.
Definition of LCD screen
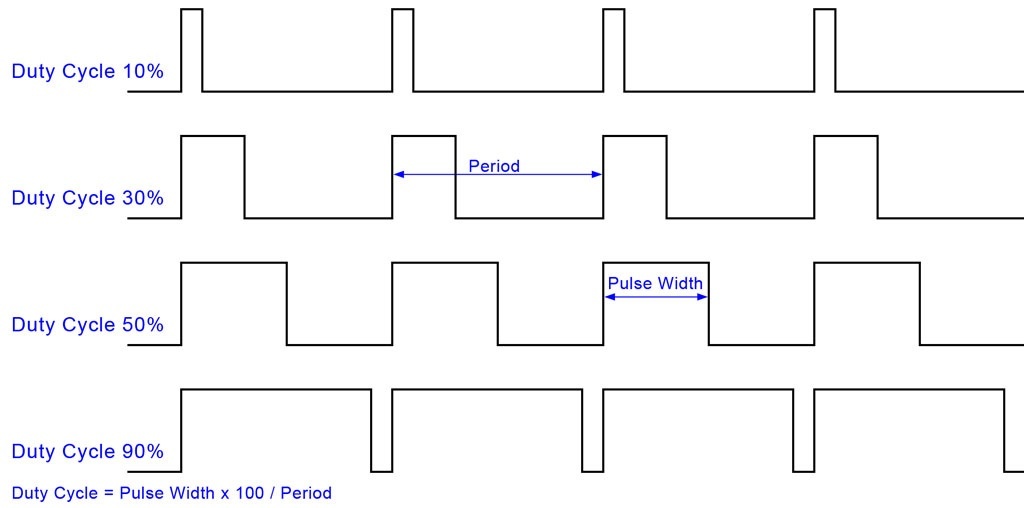
LCDs are used to display text and images in the form of dots or line segments. LCDs have liquid crystal filaments that are filled between transparent electrodes. When current is passed between the electrodes, the filament becomes energized and emits visible light.
Liquid crystals used in displays have both solid and liquid properties. When no potential is applied to the liquid crystal, it becomes transparent, but upon activation, the crystal scatters light in all directions and appears bright.
The LCD power consumption is very low and it also has a seven-segment display. But it is equivalent to an LED, which is a slower device and takes more time to switch. DC shortens their lifespan, so they are mostly used with AC at frequencies below 500 Hz.
Brief Summary
I don’t know if you have noticed that LED is a light source, while LCD is a display device. The two are obviously different.
One of the main differences between LEDs and LCDs is that LEDs use PN junction diodes that emit light when current is passed through them, while LCDs use liquid crystals or plasma to emit visible light. A liquid crystal is filled between the glass electrodes, and when power is applied to it, the liquid crystal becomes energized and emits light.
Technology Comparison
p-n node
When a p-type semiconductor is connected to an n-type semiconductor, the contact thus formed is called a p-n junction. All semiconductor devices contain one or more PN junctions. The p-n junction is actually the control element of the semiconductor device.
Formation of p-n junction
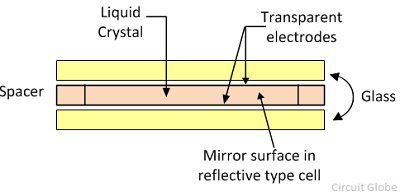
In practical applications, a PN junction is not formed simply by placing a p-type semiconductor block close to an n-type semiconductor block. In fact, p-n junctions are fabricated by special techniques, namely growth, alloying, and diffusion methods.
The most common method of making pn junctions is called alloying. Alloy junctions are made of n-type semiconductors made of germanium or silicon by melting trivalent indium particles placed on either side. The entire arrangement or system is heated to about 500 degrees Celsius. Indium is absorbed into germanium or silicon to create a p-region, thus forming a pn junction.
Another method of forming a pn junction is called diffusion. In this process, a semiconductor wafer p-type or n-type with one conductivity is placed in a container containing the impurity oxide to be added. The combination is slowly passed through a furnace controlled at a temperature of 800⁰C to 1200⁰C, depending on the type of junction. At such high temperatures, a gas of impurity atoms diffuses into the semiconductor material, forming a thin layer of opposite conductivity. Therefore, a pn junction is formed.
Either LED or LCD, can be used to display images and text. But the chemistry is not the same. LEDs use gallium arsenide and gallium phosphide, two compounds that emit visible light when heated.
When monochromatic light is displayed, it is usually used to display basic elements such as numbers and letters or some specific symbols. When there is only monochromatic light, it is still unable to display the picture or more complex patterns and other elements normally.
LCD, on the other hand, is a thin layer of liquid crystal filaments between glass electrodes. When power is applied to the electrodes, they begin to emit light energy in the form of photons. Therefore, the LCD can directly display text or images in the form of dot matrix and line segments.
Materials used
LED is a filament made of various compounds (such as aluminum gallium arsenide, indium gallium nitride, etc.), which can emit light of different colors when energized.

As for the liquid crystal materials used in LCD, this depends on the high-level subjects we have studied before. All matter with uniform motion in the world belongs to phase state. In addition to the familiar solid state and liquid state, there are also unfamiliar liquid crystal states and plasma states.
LCD uses a liquid crystal state that we are not familiar with. This material has special optical properties and is sensitive to electromagnetic fields, making it very valuable for research.
Comparing the shapes of the two, although they both belong to the phase state, LED uses solid compounds, while LCD uses liquid crystal compounds, and the two are also different.
Luminous principle
LEDs emit light autonomously, and when current passes through them, the materials of these semiconductors move evenly, creating a light source. These semiconductor materials can only emit one color of light at a time.
In order to display full-color colors, three different compounds need to be combined and energized together to produce full-color colors.
The LCD itself cannot emit light and needs to rely on a backlight to emit light, so the whole process is quite tortuous.
Depending on the liquid crystal material, there are nematic liquid crystals and smectic liquid crystals. The biggest difference between the two is that nematic liquid crystals have lower viscosity and stronger fluidity. Therefore, it is more widely used.
With the characteristics of nematic liquid crystal, only a very small force is needed to change the movement of liquid crystal molecules so that the optical axis of the liquid crystal is consistent with its molecular axis, thereby producing optical effects.
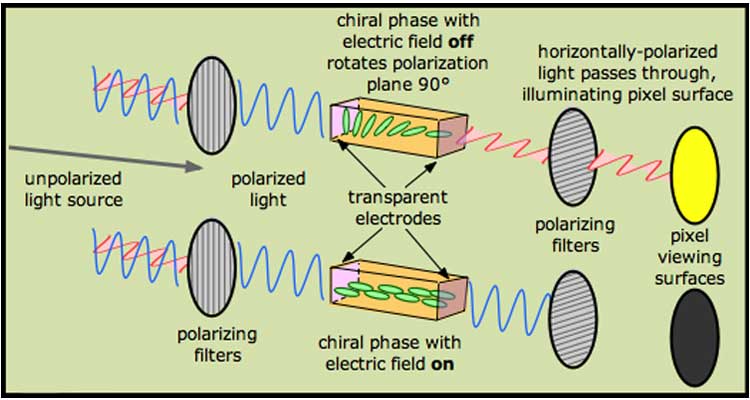
After the liquid crystal electric field is removed, the liquid crystal molecules use their elasticity and viscosity to return to their previous state, that is, the way they were before they emitted light.
LCD currently has three backlight sources: EL (electroluminescence), CCFL (cold cathode fluorescent lamp) and LED (light emitting diode).
Since the first two types have certain defects, they have been gradually replaced by LED backlights. An interesting question even arises: Is an LCD using an LED backlight an LCD or an LED? Those who are interested can think about it.
Structure
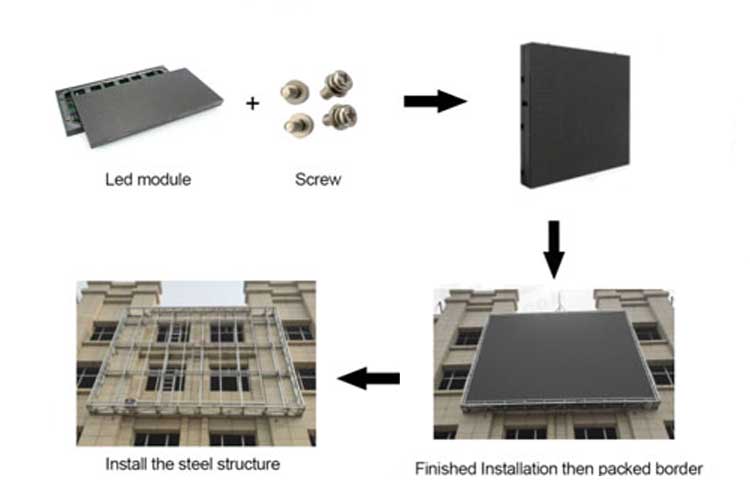
LEDs currently come in two common forms, one is plug-in and the other is surface-mounted. Although they look different in form, the structure and principle are the same. All are achieved by sealing the luminescent material in a container. After the power is turned on, a light source will be generated.
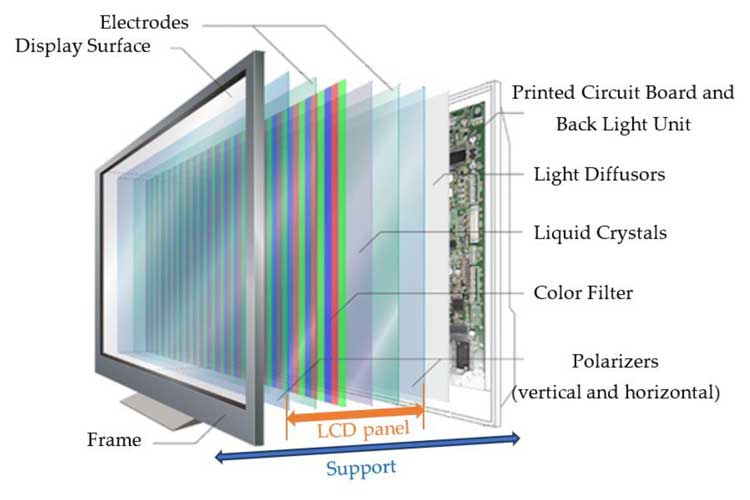
LCD is a little more complicated. It needs to put liquid crystal material into the laminated glass, and then in order to make it shine, a reflector with a light source needs to be placed on the back to provide backlight for the liquid crystal.
Summary of the first paragraph
We analyzed the differences between LED VS LCD from three aspects: material, light-emitting principle and structure. Finally, we were surprised to find that LCD now incorporates some LEDs, and the two have become inseparable.
LED VS LCD Advantage Comparison
In the previous chapter, we introduced that liquid crystal itself does not have the conditions to emit light, so we chose finished products to compare the advantages of LCD vs LED.
Contrast
Contrast is the brightness at the whitest moment/the brightness at the darkest moment. Judging from the test data, LED performs better than LCD. Even if an LCD uses an LED backlight, according to the law of conservation of energy, there will always be more or less loss when reflecting the light source, so LED is better than LCD.
Resolution
The LCD needs to be set before leaving the factory, and cannot be changed after it is set. LEDs can be spliced according to actual needs, and it is difficult to distinguish between the two. From the perspective of flexibility, LED is better, and from the perspective of simplicity, LCD is better.
Color gamut width
Wide color gamut is a color backlight technology. The international standard is that the color coverage reaches NTSC92%. The wide color gamut color coverage of most LCD screens on the market is between 92% and 109%, while the wide color gamut color coverage of LED displays is 110%. The wide color gamut color coverage of LED is slightly higher.
Screen thickness
This LCD beats the LED completely. The LCD, including the frame, can still be 8-10 mm thick, while the splicing modules in most LED displays are 5 cm thick and require additional cabinets to function properly. Installed, the average thickness reached 20 cm.
Although a few types of LED displays (such as transparent LED displays) do not have the thickness of modules, they still have the thickness of a cabinet, so there is still a certain gap compared with LCDs.
Energy saving
Energy saving is the strength of LED, and it is precisely for this reason that only the LED backlight remains among the three commonly used LCD backlight sources.
Service life
The average service life of LEDs is about 11 years, but LCDs only have a service life of 7–9 years.
Cost
This is one of the few strengths of LCD. For the same 100-inch display screen, if the LED display screen wants to achieve the clarity of LCD, the cost will be 3–5 times.
In other words, if a 100-inch LCD screen costs 2,000 US dollars, then the LED display screen will cost at least 6,000-10,000 US dollars.
Technology maturity
At present, both of them have experienced more than 10 years of development, and their technical maturity is very high, and they can achieve various customized effects.
Summary of the second paragraph
We analyzed the advantages of LED and LCD from multiple aspects such as contrast, resolution, wide color gamut, price, etc. We can find that although LED almost completely beats LCD, there is still an insurmountable gap in the field of small display devices.
Application Area
Indoor Application
Monitoring room

Because LED displays have better display effects, more flexible performance, and strong integration, many monitoring rooms have replaced LCDs with LED displays.
Meeting room

Compared with the monitoring room, the conference room does not have high requirements for screens. In order to save costs, the conference room still mainly uses LCD equipment.
TV

Although LED display screens can be used as rear-projection TVs, and LED materials can also be used to customize TVs, they are much more expensive than LCD TVs, so LCD TVs are still the mainstream.
Outdoor Application
Most of the outdoor advertising market is covered by LED displays, leaving only some platforms and stores using LCDs. On the one hand, these scenes do not have high requirements for display, and on the other hand, the scene area is not large. , the use of LED displays is overkill.

Advantages of LED display in outdoor applications
- Flexible splicing: LED displays are very flexible in splicing, and in theory, as long as you have enough money, you can even have unlimited splicing. This kind of flexible splicing can well meet different outdoor areas.
- Low maintenance cost: Once there is a problem with the LCD, the entire screen often needs to be replaced, but the usually LED only has a certain LED module failure. At this time, you only need to replace it with an LED module of the same model to display normally. . The maintenance cost will be much lower than that of LCD.
- High brightness: Due to strong sunlight outdoors, the brightness of ordinary display devices is not high enough, which will cause the screen to become blurry. However, the LED display can reach a brightness of 7000 or even 8000, so it does not affect the viewing experience under the sun. .
- Waterproof: If the LCD is placed for outdoor use, the entire screen needs to be completely enclosed with glass or acrylic plates, otherwise the screen will be easily damaged due to water intrusion. The LED display screen is specially designed for outdoor use. From the LED module to the LED cabinet, it is designed to be waterproof and hydrophobic, which can effectively prevent rainwater from penetrating and causing screen damage.
The main difference between LED and LCD
- An LED is a PN junction diode that emits visible light when a forward bias is applied to it. LCDs use liquid filaments that are filled between glass electrodes to emit light.
- LED stands for Light Emitting Diode while LCD stands for Liquid Crystal Display
- LCDs use cold cathode fluorescent lamps to provide backlighting for the screen, and LEDs use PN junction diodes to display light. Backlighting refers to turning the display on and off for better viewing.
- The scalability of LED is very strong, so the resolution is much better than LCD, and it is easy to implement, so many 4K and 8K displays are being converted from LCD to LED. Resolution is the number of pixels on the screen display.
- Due to the plasma, LEDs consume more power compared to LCDs. Filaments used in LCDs consist of plasma, which requires less power to activate.
- LEDs have a smaller display area compared to LCDs because LEDs use PN junction diodes that display light in only one direction, while LCDs light up in all directions. However, after the LED is made into an LED display, it can be spliced in an infinite area, while the LCD can only be made according to the specified size, and cannot be spliced in an infinite area.
- Compared with LCD, to achieve the same picture effect, the cost of LED is higher.
- LEDs use gallium arsenide, which emits light when heated, while LCDs use liquid crystals that energize and provide light.
- LEDs have shorter switching times compared to LCDs. Toggle times are their displayed activation and deactivation times.
- DC will shorten the lifespan of LCDs, while LEDs have no effect.
- Compared to LCD, LED has a lower contrast ratio. The contrast ratio is the ratio of the brightness of the visible light to the darker light on the screen.
- LCDs use mercury, which pollutes the environment, while LEDs do not.
Both LED and LCD are modern technologies. Neither is the strongest, only which is more suitable.
Summarize
The above is the detailed introduction of LED vs LCD. We have conducted detailed analysis from many different angles. I believe that the above article can help you distinguish the difference between the two.




